What is GPU Server?
What is a GPU Server?
In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, GPU servers have become increasingly important. These powerful machines are central to advancements in artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, scientific research, and more. But what exactly is a GPU server, and why is it so crucial? This article delves into the fundamentals of GPU servers, their components, applications, and advantages.
Understanding GPU Servers
Definition of a GPU Server
A GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) server is a type of server equipped with one or more GPUs. Unlike traditional servers that rely solely on CPUs (Central Processing Units) for processing tasks, GPU servers leverage the parallel processing capabilities of GPUs to handle complex computations more efficiently. This combination allows for handling a broad range of tasks, from graphical rendering to intensive computational workloads.
Components of a GPU Server
A typical GPU server comprises several key components:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The brain of the server, responsible for general-purpose computing tasks and overall system management.
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit): Specialized hardware designed to perform parallel processing, ideal for tasks involving massive datasets and complex calculations.
- Memory (RAM): Temporary storage that provides quick access to data for the CPU and GPU.
- Storage: Long-term data storage, including SSDs (Solid State Drives) and HDDs (Hard Disk Drives), for storing large datasets and applications.
- Motherboard: The central circuit board connecting all components, including the CPU, GPU, memory, and storage.
- Power Supply: Provides the necessary power to run the server’s components.
- Cooling System: Essential for maintaining optimal operating temperatures, preventing overheating, and ensuring stable performance.
How GPUs Differ from CPUs
While both CPUs and GPUs are integral to computing, they are designed for different types of tasks. CPUs are optimized for single-threaded performance, making them suitable for general-purpose processing and tasks requiring sequential execution. GPUs, on the other hand, excel at parallel processing, handling thousands of simultaneous threads. This makes them ideal for tasks such as:
- Rendering graphics and images
- Processing large datasets
- Performing complex mathematical computations
Applications of GPU Servers
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
One of the most prominent applications of GPU servers is in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Training AI models requires immense computational power to process large datasets and perform numerous calculations. GPUs accelerate these processes, significantly reducing the time required for training and inference. Applications in this domain include:
- Natural language processing (NLP)
- Computer vision
- Autonomous vehicles
- Recommendation systems
Scientific Research
GPU servers are also pivotal in scientific research, enabling researchers to perform simulations and analyze data at unprecedented speeds. Fields such as genomics, climate modeling, and physics simulations benefit from the enhanced computational capabilities of GPUs. Examples include:
- Molecular dynamics simulations in drug discovery
- Weather prediction models
- Astrophysical simulations
Data Analytics
In data analytics, GPU servers enable the processing of vast amounts of data quickly and efficiently. This capability is crucial for businesses and organizations that rely on real-time data analysis to make informed decisions. Use cases include:
- Financial modeling and risk assessment
- Fraud detection
- Market trend analysis
Rendering and Content Creation
For industries involved in rendering and content creation, such as film production, animation, and game development, GPU servers provide the necessary power to render high-quality graphics and visual effects. They enable:
- Real-time rendering of 3D graphics
- Video encoding and decoding
- Complex visual effects processing
Advantages of GPU Servers
Enhanced Performance
The primary advantage of GPU servers is their ability to perform complex computations much faster than traditional CPU-only servers. This enhanced performance is due to the parallel processing capabilities of GPUs, which can handle multiple tasks simultaneously.
Cost-Effectiveness
While GPUs are often more expensive than CPUs, the cost savings come from the reduced time required to complete computational tasks. This efficiency translates to lower operational costs, particularly in environments where processing time is a critical factor.
Scalability
GPU servers offer excellent scalability, allowing organizations to add more GPUs as needed to handle increasing workloads. This scalability ensures that businesses can grow their computational resources in line with their needs, without overhauling their entire infrastructure.
Energy Efficiency
Modern GPUs are designed to be energy-efficient, providing high performance while consuming less power compared to an equivalent number of CPUs. This energy efficiency is beneficial for data centers and organizations aiming to reduce their carbon footprint.
Versatility
GPU servers are versatile and can be used across various industries and applications. Whether for AI and machine learning, scientific research, data analytics, or content creation, GPU servers provide the necessary computational power to handle diverse and demanding tasks.
Challenges and Considerations
Initial Investment
One of the primary challenges associated with GPU servers is the initial investment. High-performance GPUs can be expensive, and setting up a GPU server requires significant capital. However, the long-term benefits and cost savings often outweigh the initial expenditure.
Integration and Compatibility
Integrating GPU servers into existing infrastructures can be complex, requiring careful planning and consideration of compatibility with existing systems and software. Ensuring seamless integration is crucial for maximizing the benefits of GPU servers.
Maintenance and Cooling
Maintaining optimal performance and temperature levels is essential for GPU servers. Effective cooling systems and regular maintenance are necessary to prevent overheating and ensure the longevity of the hardware.
Conclusion
GPU servers represent a significant advancement in computing technology, offering unparalleled performance and efficiency for a wide range of applications. Their ability to handle complex computations and large datasets makes them indispensable in fields such as AI, scientific research, data analytics, and content creation. While there are challenges associated with their initial investment and integration, the benefits of enhanced performance, cost-effectiveness, scalability, and energy efficiency make GPU servers a worthwhile investment for organizations aiming to stay at the forefront of technological innovation. As technology continues to evolve, GPU servers will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping the future of high-performance computing.

 When AI Becomes A Threat, Infrastructure Becomes the Front Line
When AI Becomes A Threat, Infrastructure Becomes the Front Line
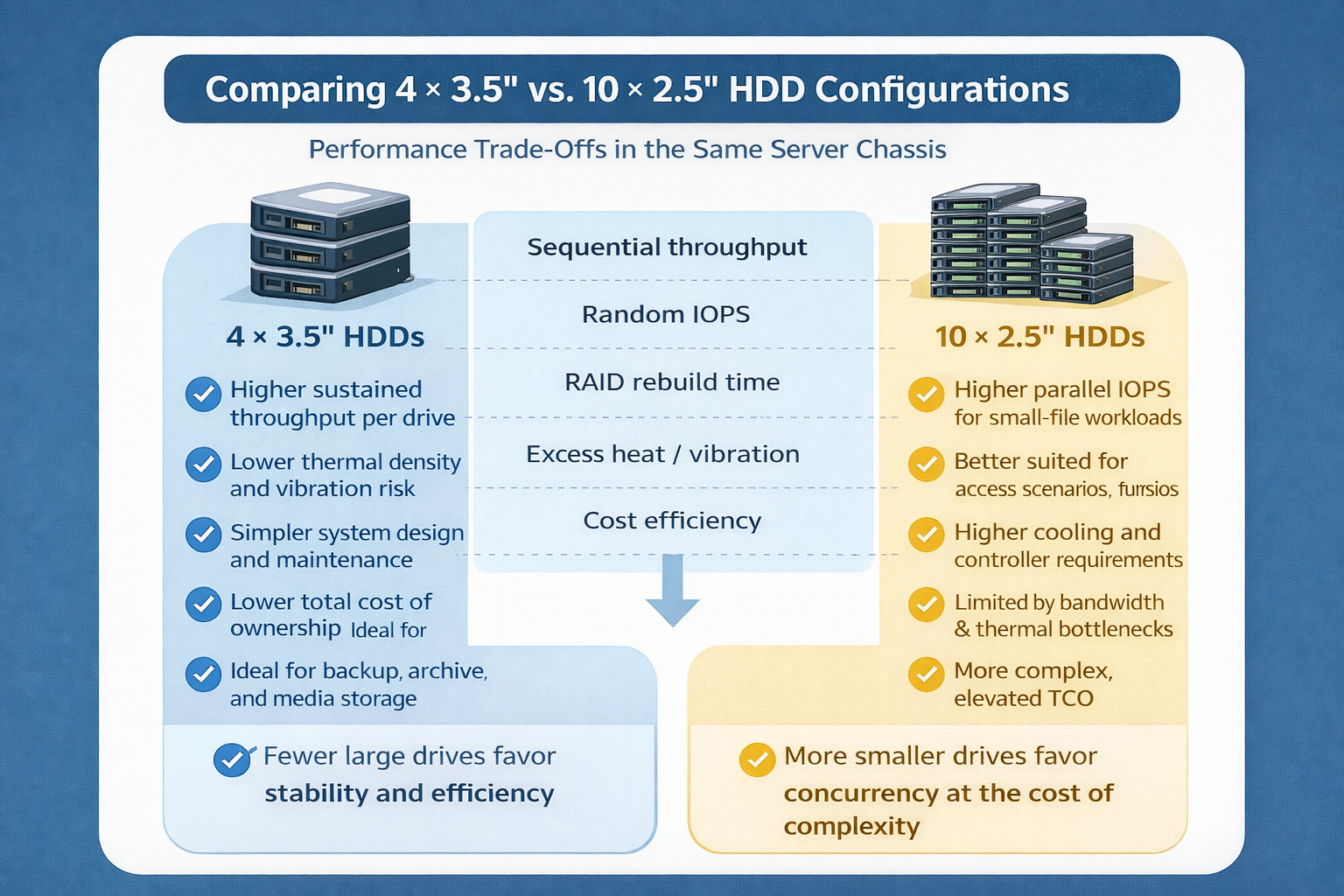 Storage Density Choices in the Same Server Chassis
Storage Density Choices in the Same Server Chassis
 Welcoming 2026: Building the Next Year of AI Infrastructure Together
Welcoming 2026: Building the Next Year of AI Infrastructure Together
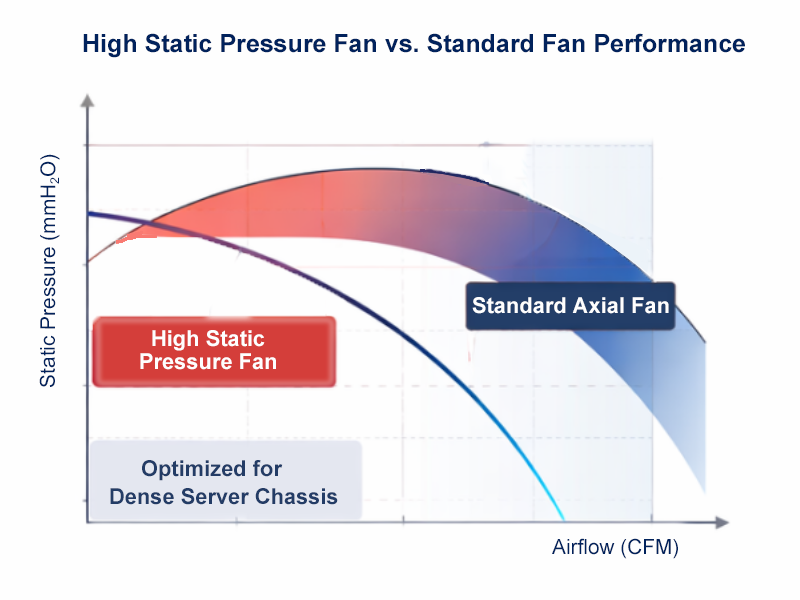 How We Design Thermal Paths: Airflow, Static Pressure & Fan Zones
How We Design Thermal Paths: Airflow, Static Pressure & Fan Zones

